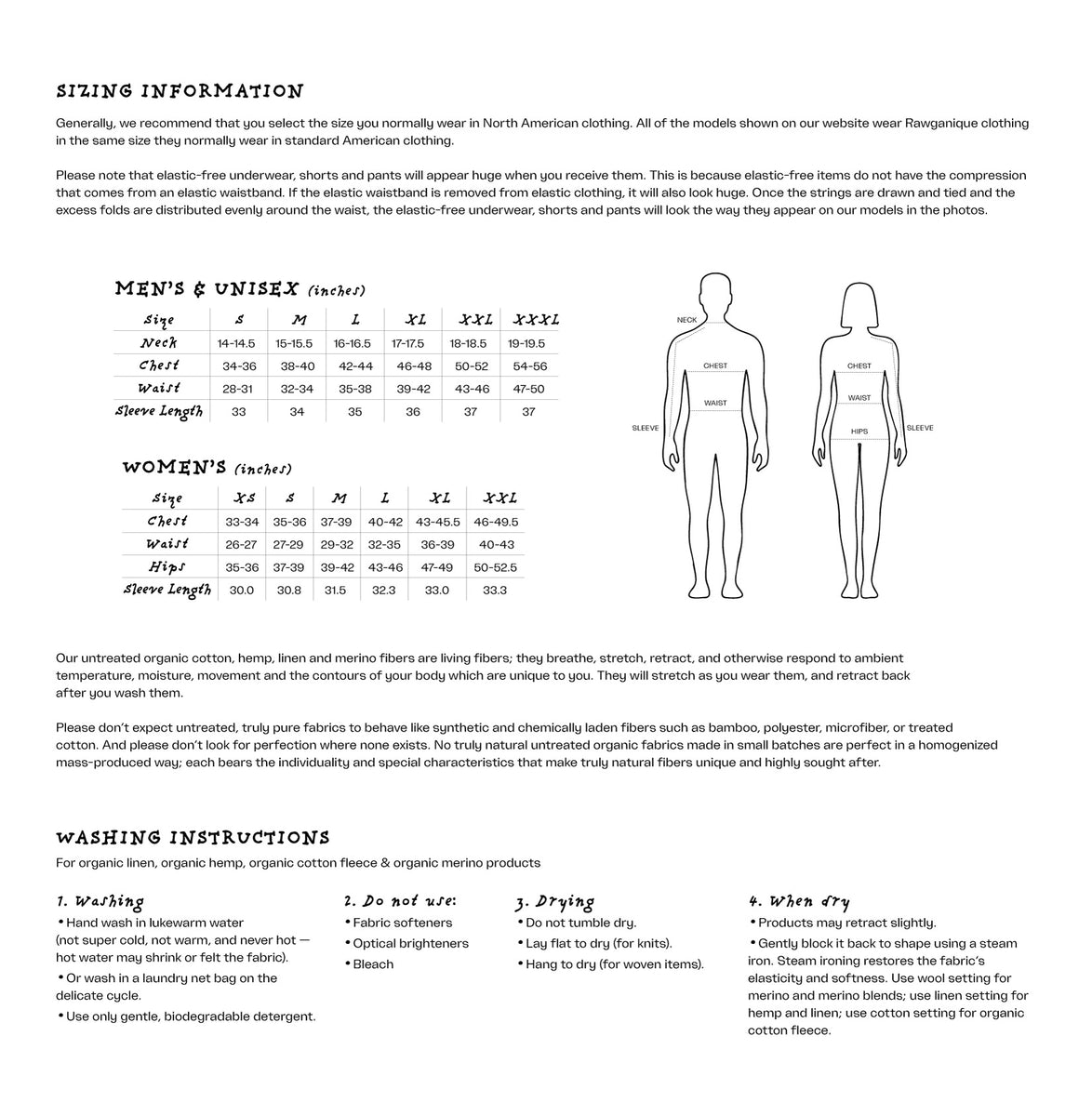
Hemp Information
Hemp fiber makes for comfortable, durable, stylish and distinctive clothing (but it's not just the comfort that makes hemp fiber clothing special -- please read on to find out why), and hemp seeds make for highly nutritious and utterly delicious foods, teeming with live enzymes and many other essential nutrients like chlorophyll. The hemp plant is an easy-to-grow annual plant that doesn't require pesticides or herbicides to thrive. It is truly mind-boggling to think what the world would be like in just a few years if, for instance, half of the world's paper supply comes from hemp fiber instead of trees. It is completely within our power to effect this change. By taking the decision to add hemp to our lives, we are voting with our money and showing our commitment to the health and well-being of our planet as well as ourselves. It's a fragile planet, let us tread it with care.
organic hemp oil
The following is excerpted from the mind-boggling and eye-opening book The Emperor Wears No Clothes by Jack Herer, a must-have book for anyone who cares about the future and well-being of our fragile planet. This visionary book makes clear why it is necessary to add hemp to our individual and collective lives today and why hemp is essential to our well-being as well as that of the earth.
Hemp is sustainable clothing, footwear, shelter, foods, tree-free paper, cement, gasoline, fuel, nutritious and delicious foods, paint, industrial sealants, industrial composites, and so much more. Its beauty, usefulness, and astounding versatility truly boggle the mind! Hemp oil, for example, has the highest percentage of usable essential fatty acids of any plant, period.
Why hemp? Because it is, by far, Earth's premier, renewable natural resource. The hemp plant can single-handedly reverse the Greenhouse Effect, purify our air, water, & soil, and clothe and shelter us in a sustainable fashion.
Hemp paper lasts 50 to 100 times longer than most preparations of papyrus and is a hundred times easier and cheaper to make. It also does not yellow with age like acidic paper made from tree pulp.
If the hemp pulp paper process of 1916 were in use today, it could replace 40 to 70% of all pulp paper (from trees), including corrugated boxes, computer printout paper and paper bags. Imagine the effect this conversion to hemp paper alone would have on near-extinct species and all forms of wild life, on old-growth forests that are fast disappearing, on the quality of our water, air, and soil, as well as on our planet's sensitive ecosystem! (Thanks to Eric DaHemp Man, who has compiled hemp's many histories throughout the world, we are able to share several interesting images in this section, including the following one of a hemp seed sprouting, which we posted on social media as follows: The hemp life force: A teeny little seed pushing its way through the earth to grow 8-12 feet in a matter of months, yielding so many beautiful possibilities: clothes, foods, footwear, construction materials, paper, and SO MUCH MORE. How's that for basic, primordial instinct? Thanks, Eric.)
hemp cannabis sativa information
Hemp stems are 80% hurds (pulp byproduct after the hemp fiber is removed from the plant). Hemp hurds are 77% cellulose--a primary chemical feed stock (industrial raw material) used in the production of chemicals, plastics, and fiber. An acre of full grown hemp plants can sustainably provide from four to 50 or even 100 times the cellulose found in cornstalks, kenaf, or sugar cane--the planet's next highest annual cellulose plants.
Hemp will grow in any state in the US and most of Canada. In most places, hemp can be harvested twice a year and, in warmer areas such as southern California, Texas, Florida and the like, it could be a year-round crop. Hemp has a short growing season and can be planted after food crops have been harvested.
Farming only 6% of continental US acreage with biomass crops would provide all of America's gas and oil energy needs, ending dependence upon fossil fuels.
Hemp is Earth's number-one biomass resource; it is capable of producing 10 tons per acre in four months. Hemp is easy on the soil, sheds its lush foliage throughout the season, adding mulch to the soil and helping retain moisture. Hemp is an ideal crop for the semi-arid West and open range land.
Hemp is the only biomass source available that is capable of making the US energy-independent. Ultimately, the world has no other rational environmental choice but to give up fossil fuels.
hemp cannabis sativa information
From the farmers' point of view, hemp is an easy crop to grow and will yield from three to six tons per acre on any land that will grown corn, wheat, or oat. It has a short growing season, so that it can be planted after other crops are in. It can be grown in any state of the union. Hemp's long roots penetrate and break the soil to leave it in perfect condition for the next year's crop. The dense shock of leaves, eight to twelve feet above the ground, chokes out weeds, eliminating the need for chemicals or pesticides, 50% of which is used today on conventionally-grown cotton plant alone to produce cotton clothing products that are inferior to hemp clothing in terms of durability, thickness, softness, and sustainability. Two successive hemp crops are enough to reclaim land that has been abandoned because of Canadian thistles or quack grass
The earliest known woven fabric was apparently of hemp, which began to be worked in the eighth millennium (8,000-7,000 BC)."
From more than 1,000 years before the time of Christ until 1883 AD, cannabis hemp--indeed, marijuana--was our planet's largest agricultural crop and most important industry, involving thousands of products and enterprises; producing the overall majority of Earth's fiber, fabric, lighting oil, paper, incense, and medicines. In addition, it was a primary source of essential food oil and protein for humans and animals.
Ninety percent of all ships' sails (since before the Phoenicians, from at least the 5th Century BC until long after the invention and commercialization of steam ships--mid- to late-19th century) were made from hemp.
The word "canvas" is the Dutch pronunciation (twice removed, from French and Latin) of the Greek word "Kannabis."
In addition to canvas sails, until this century virtually all of the rigging, anchor ropes, cargo nets, fishing nets, flags, shrouds, and oakum (the main protection for ships against salt water, used as a sealant between loose or green beams) were made from the stalk of the marijuana plant. (Here's another set of images compiled by Eric; this one of hemp's place in botanical history in different cultures and languages.)
hemp botanical history
Even the sailors' clothing, right down to the stitching in the seamen's rope-soled and "canvas" shoes, was crafted from cannabis.
Additionally, the ships' charts, maps, logs, and Bibles were made from paper containing hemp fiber from the time of Columbus (15th century) until the early 1900s in the Western European/American world, and by the Chinese from the 1st Century AD on.
Until the 1820s in America (and until the 20th Century in most of the rest of the world), 80% of all textiles and fabrics used for clothing, tents, bed sheets, and linens, rugs, drapes, quilts, towels, diapers, etc.--and even the US flag, "Old Glory," were principally made from fibers of cannabis hemp.
From 70-90% of all rope, twine, and cordage was made from hemp until 1937. It was then regrettably replaced mostly by petrochemical fibers, but at what untold costs to the environment?
Hemp is the perfect archival medium for artists' work, because it is acid-free. The paintings of Van Gogh, Gainsborough, Rembrandt, etc., were primarily painted on hemp canvas, as were practically all canvas paintings.
A strong, lustrous fiber, hemp withstands heat, mildew, insects, and is not damaged by light. Oil paintings on hemp and/or flax canvas have stayed in fine condition for centuries.
For thousands of years, virtually all good paints and varnishes were made with hempseed oil and/or linseed oil.
Until about 1800, hempseed oil was the most consumed lighting oil in America and the world. From then until the 1870s, it was the second most consumed lighting oil, exceeded only by whale oil. (Another historical image; this one of hemp harvest.)
hemp hay field
Hempseed oil lit the lamps of the legendary Aladdin, Abraham the prophet, and in real life, Abraham Lincoln. It was the brightest lamp oil.
In the early 1900s, Henry Ford and other futuristic, organic, engineering geniuses recognized (as their intellectual, scientific heirs still do today) an important point--that up to 90% of all fossil fuel used in the world today (coal, oil, natural gas, etc.) should long ago have been replaced with biomass such as : cornstalks, cannabis sativa (hemp), waste paper and the like.
Biomass can be converted to methane, methanol or gasoline at a fraction of the current cost of oil, coal, or nuclear energy--especially when environmental costs are factored in--and its mandated use would end acid rain, end sulfur-based smog, and reverse the Green house Effect on our planet--right now!
Hempseed can be pressed for its highly nutritious vegetable oil, which contains the highest amount of essential fatty acids in the plant kingdom.
Because one acre of hemp produces as much cellulose fiber pulp as 4.1 acres of trees, hemp is the perfect material to replace trees for pressed board, particle board and for concrete construction molds. (We love, love, love historical re-enactments because we learn so much from them. We are fascinated by how everyday things were done before the age of chemicals and industrializaton. This image from Eric's collection depicts sewing, mending of hemp clothing and fabrics. We have many customers who use our organic hemp ropes, fabrics, pirate shirt, and other clothing in historical re-enactments, battlefield depictions, and reproduction harpoons.)
hemp historical reenactment
Practical, inexpensive fire-resistant construction material, with excellent thermal and sound-insulating qualities, is made by heating and compressing hemp fibers to create strong construction paneling, replacing dry wall and plywood. William B. Conde of Conde's Redwood Lumber, Inc, near Eugene, OR, has demonstrated the superior strength, flexibility, and economy of hemp composite building materials compared to wood fiber, even as beams.
Iso-chanvre (chanvre is French for hemp), a rediscovered French building material made form hemp hurds mixed with lime, actually petrifies into a mineral state and lasts for many centuries. Archeologists have found a bridge in the south of France, from the Merovingian period, built with this process.
Hemp has been used throughout history for carpet backing. Hemp fiber has potential in the manufacture of strong, rot-resistant carpeting--eliminating the poisonous fumes of burning synthetic materials in a house or commercial fire, along with allergic reactions associated with new synthetic carpeting, which may outgas volatile toxic fumes for months or even years, endangering human health.
Plastic plumbing pipes (PVC pipes) can be manufactured using renewable hemp cellulose as the chemical feedstocks, replacing nonrenewable coal or petroleum-based chemical feedstocks.
So we can envision a house of the future built, plumbed, painted, and furnished with the world's number-one renewable resource--hemp.
We believe that in a competitive market, with all facts known, people will rush to buy long-lasting, biodegradable "Pot Tops" or "Mary Jeans," etc, made from hemp grown without pesticides or herbicides.
It's time we put capitalism to the test and let the unrestricted market of supply and demand as well as "Green" ecological consciousness decide the future of the planet.
A cotton shirt in 1776 cost $100 to $200, while a hemp shirt cost $0.50 to $1. By the 1830s, cooler, lighter cotton shirts were on par in price with the warmer, heavier, hempen shirts, providing a competitive choice, thanks to government subsidies.
(Another piece of hemp history, thanks to Eric.)
hemp fields
People were able to choose their garments based upon the particular qualities they wanted in a fabric. Today we have no such choice. Conventional cotton growing, which depletes and pollutes our nonrenewable resources, is still heavily subsidized by the government, masking the true costs of production and costs to the environment, whereas hemp is not allowed to be grown at all in the US (hopefully this is changing, for our planet's sake!).
The role of hemp and other natural fibers should be determined by the market of supply and demand and personal tastes and values, not by the undue influence of prohibition laws, federal subsidies and huge tariffs that are designed to keep the natural fabrics from replacing synthetic fibers.
Sixty years of government suppression of information has resulted in virtually no public knowledge of the incredible potential of the hemp fiber or its uses.
By using 100% hemp or mixing hemp with cotton, you will be able to pass on your shirts, pants, and other clothing to your grandchildren. Intelligent spending could essentially replace the use of petrochemical synthetic fibers such as nylon and polyester with tougher, cheaper, cool, absorbent, breathable, biodegradable natural fibers such as hemp and flax.
China, Italy and East European countries such as Hungary, Romania, Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Russia currently make millions of dollars worth of sturdy hemp and hemp/cotton textiles--and could be making billions of dollars worth--annually.
These countries build upon their traditional farming and weaving skills, while the US tries to force the extinction of the hemp plant in the attempt to promote destructive synthetic technologies.
Additionally, hemp grown for biomass could fuel a trillion-dollar-per-year energy industry, while improving air quality and distributing the wealth to rural areas and their surrounding communities, and away from centralized power monopolies. More than any other plant on Earth, hemp holds the promise of a sustainable ecology and economy.
(Images like these make one wonder why hemp is not grown everywhere right now. Why is it even illegal in some places?? It's such a useful plant!!! — again, from Eric's collection.)
hemp fields
If all fossil fuels and their derivatives, as well as trees for paper and construction were banned in order to save the planet, reverse the Greenhouse Effect and stop deforestation...
Then there is only one known, annually renewable natural resource that is capable of providing the overall majority of the world's paper and textiles; meeting all of the world's transportation, industrial and home energy needs, while simultaneously reducing pollution, rebuilding the soil, and cleaning the atmosphere all at the same time...
And that substance is--the same one that did it all before--Cannabis Hemp!
Hempseed is the highest of any plant in essential fatty acids.
Hempseed oil is among the lowest in saturated fats at 8% of total oil volume. The oil pressed from hempseed contains 55% linoleic acid (LA) and 5% linolenic acid (LNA). Only flax oil has more linolenic acid at 58% , but hempseed oil is the highest in total essential fatty acids at 80% of total oil volume.
These essential fatty acids are responsible for our immune response.
In the old country the peasants ate hemp butter. They were more resistant to diseases than the nobility, who shunned hemp butter as peasant food.
LA and LNA are involved in producing life energy from food and the movement of that energy throughout the body.
Essential fatty acids govern growth, vitality and state of mind. LA and LNA are involved in transferring oxygen from the air in the lungs to every cell in the body. They play a part in holding oxygen in the cell membrane where it acts as a barrier to invading viruses and bacteria, neither of which can thrive in the presence of oxygen.